What are Electrical Breakers and Their Role in Electrical Safety Standards
Electrical safety is a paramount concern in modern societies, and electrical breakers play an essential role in ensuring this safety. Understanding what electrical breakers are and how they function within the broader context of electrical safety standards is crucial for both homeowners and professionals in the industry. These protective devices are designed to interrupt the flow of electricity in the case of an overload or short circuit, thus preventing potential hazards such as electrical fires and equipment damage. As we delve into the importance of electrical breakers, we will explore how they contribute to the overall safety framework, their various types, and the standards that govern their implementation. This examination will illuminate why investing in the right electrical breakers is not only a smart decision but also a critical step in safeguarding lives and properties from electrical risks.

Understanding Electrical Breakers: A Key Component in Safety
Electrical breakers play a pivotal role in enhancing safety standards within electrical systems. These devices are designed to automatically interrupt electrical current flow when a fault is detected, thereby protecting both equipment and personnel from hazards such as electrical shocks or fire risks. Recent advancements in circuit protection technology have underscored their importance. For instance, the global market for circuit breakers is projected to reach USD 13.12 billion by 2033, fueled by increasing electricity demand and modernization of infrastructure.
Moreover, new challenges arise with the advent of advanced battery applications, which require high-performance circuit protection solutions to ensure safety and reliability. Recent news highlights the recall of certain circuit breakers due to safety hazards, emphasizing the necessity for rigorous quality standards in their design and manufacturing. As innovations continue, devices like generator circuit breakers (GCB) are increasingly utilized to safeguard critical assets by effectively clearing dangerous short-circuit faults in power plants, reinforcing the vital role that electrical breakers play in maintaining safety across electrical networks.
The Functionality of Electrical Breakers in Modern Wiring Systems
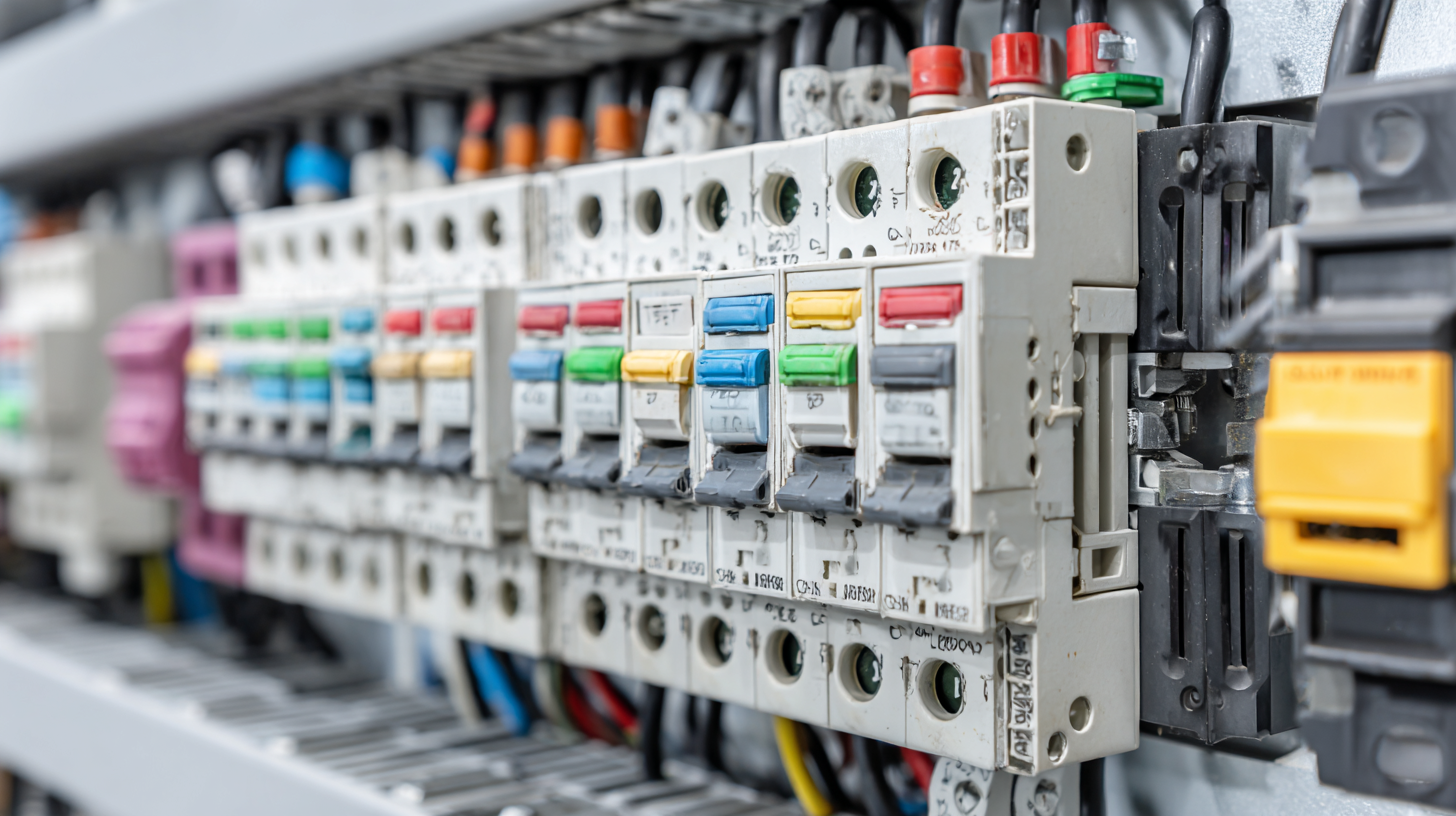 Electrical breakers serve as crucial components in modern wiring systems, ensuring safety and functionality. Their primary role is to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits, which can lead to dangerous situations such as electrical fires. When the electrical current exceeds safe levels, the breaker automatically interrupts the flow of electricity, preventing damage to both the wiring and connected appliances. This automatic response is essential for maintaining the integrity of electrical installations in homes and businesses.
Electrical breakers serve as crucial components in modern wiring systems, ensuring safety and functionality. Their primary role is to protect electrical circuits from overloads and short circuits, which can lead to dangerous situations such as electrical fires. When the electrical current exceeds safe levels, the breaker automatically interrupts the flow of electricity, preventing damage to both the wiring and connected appliances. This automatic response is essential for maintaining the integrity of electrical installations in homes and businesses.
Tips: Regularly check your electrical breakers to ensure they are functioning properly. If a breaker trips frequently, it may indicate an underlying issue that needs professional attention. It’s also wise to label each breaker in your panel, as this will help you quickly identify which circuit belongs to which part of your home, making troubleshooting easier.
In modern wiring systems, breakers are designed with user-friendly interfaces and advanced technology to enhance their performance. Some systems even feature smart breakers that can integrate with home automation systems, allowing for remote monitoring and control. This level of sophistication not only improves safety but also contributes to energy efficiency by helping users manage their power consumption effectively.
Tips: Consider upgrading to smart breakers if you are interested in energy management; they can provide insights into your usage patterns and help cut down on unnecessary expenses. Always ensure that any electrical work or upgrades are conducted by qualified professionals to maintain compliance with safety standards.
Regulatory Standards Governing Electrical Breaker Safety
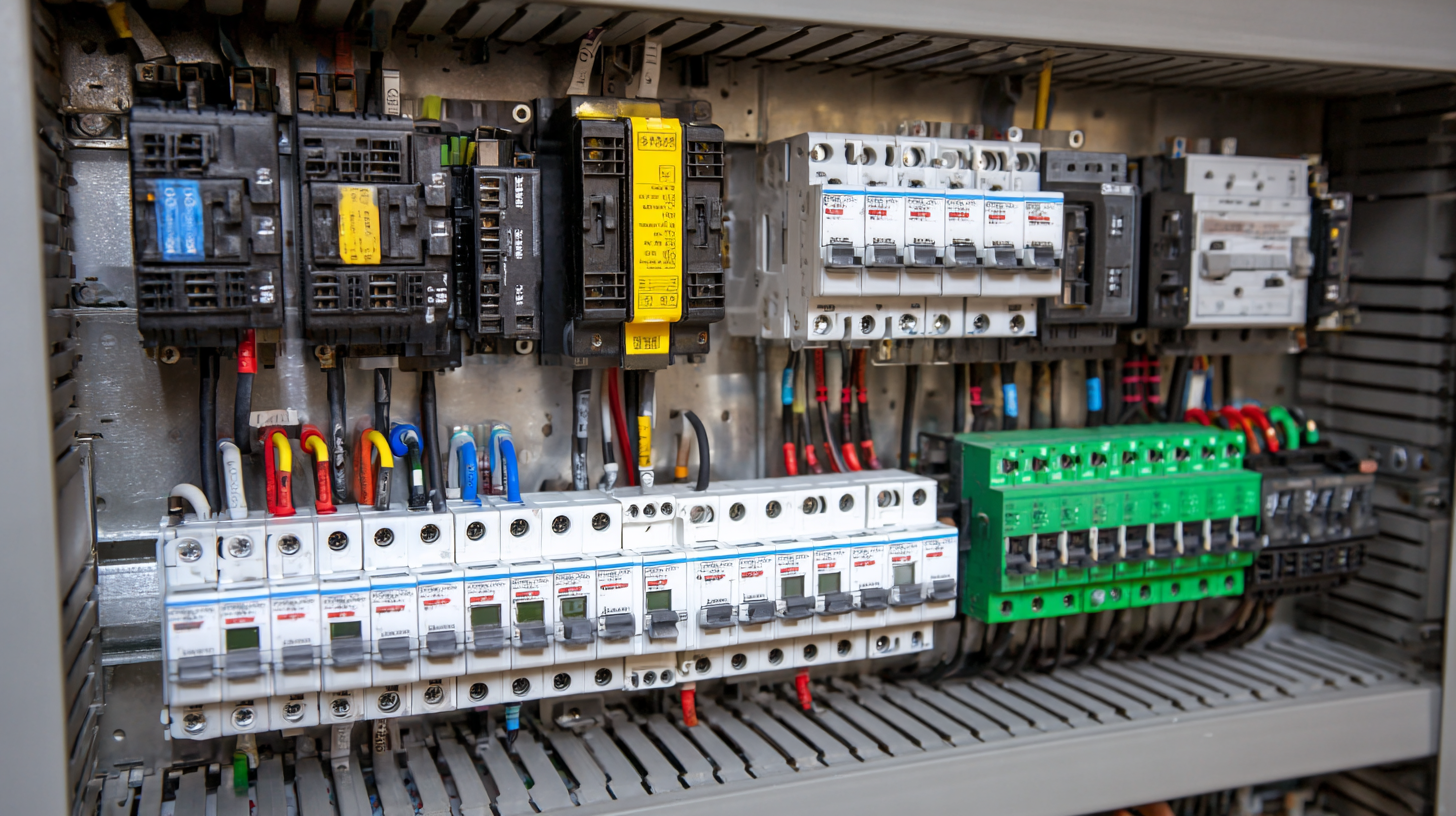 Electrical breakers are pivotal in ensuring safety within electrical systems. Regulatory standards governing electrical breaker safety are critical in minimizing risks such as electrocution and fire hazards. Organizations like the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and Underwriters Laboratories (UL) provide guidelines and certifications that define the efficacy and reliability of electrical breakers. According to a report by the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), nearly 60% of electrical fires can be attributed to failures in circuit protection devices, underscoring the importance of adhering to these regulations.
Electrical breakers are pivotal in ensuring safety within electrical systems. Regulatory standards governing electrical breaker safety are critical in minimizing risks such as electrocution and fire hazards. Organizations like the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and Underwriters Laboratories (UL) provide guidelines and certifications that define the efficacy and reliability of electrical breakers. According to a report by the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), nearly 60% of electrical fires can be attributed to failures in circuit protection devices, underscoring the importance of adhering to these regulations.
While these standards set the foundation for safety, it is vital for users and installers to be proactive. One tip is to always check for UL or CE marks on breakers, ensuring they meet rigorous safety criteria. Additionally, regular inspections can help identify wear and tear, which is crucial, as a study from the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI) revealed that 25% of home electrical fires are due to faulty equipment.
Electrical safety is not just about compliance; it is about risk reduction. Ensuring your breakers comply with the latest NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code) and staying updated on local regulations can prevent potential disasters. Remember, when dealing with electrical systems, prioritize safety and always consult with a licensed professional when in doubt.
The Role of Circuit Breakers in Preventing Electrical Hazards
Circuit breakers play a crucial role in maintaining electrical safety standards, effectively preventing electrical hazards that can lead to fires and other dangerous situations. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical failures or malfunctions account for roughly 13% of all house fires in the United States. By automatically cutting off the electrical supply during overloads or short circuits, circuit breakers significantly reduce the risk of overheating and potential ignitions, showcasing their vital function in fire prevention strategies.
Moreover, the implementation of modern circuit breaker technology enhances safety standards even further. Devices such as Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) and Arc Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) are designed to detect and respond to specific conditions that may lead to electrical hazards. A report by Underwriters Laboratories indicates that homes equipped with AFCIs can reduce the risk of electrical fires by over 50%. Therefore, integrating advanced circuit breakers into home electrical systems is essential not only for compliance with safety regulations but also for proactively protecting lives and property during Fire Prevention Month and beyond.
Comparing Different Types of Electrical Breakers for Optimal Protection
Electrical breakers play a vital role in maintaining electrical safety standards by protecting circuits from overload and short circuits. There are several types of electrical breakers, each designed for specific applications and levels of protection. The main types include miniature circuit breakers (MCBs), residual current devices (RCDs), and miniature residual current devices (MRCDs). According to a report by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), MCBs account for approximately 63% of the circuit protection market, reflecting their widespread adoption in residential and commercial installations due to their reliability and efficiency.
On the other hand, RCDs are particularly important for preventing electric shock, as they can detect imbalances in electrical currents. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) estimates that RCDs can reduce the risk of fatal electric shocks by up to 70%, making them essential in wet areas like bathrooms and kitchens. MRCDs combine the functionalities of MCBs and RCDs, offering both overload protection and shock prevention, which is why their popularity is increasing, especially in modern electrical installations. Selecting the appropriate type of breaker based on the specific environment and application is crucial for optimizing protection and adhering to safety standards.
Comparing Different Types of Electrical Breakers for Optimal Protection
This chart illustrates the effectiveness of various types of electrical breakers in providing protection against overcurrent and short circuits. The data reflects the average response time and efficiency rating of each type.
Related Posts
-

9 Essential Tips for Maintaining Your Electrical Breakers
-

Essential Checklist for Choosing the Right Motor Starters in Global Supply Chains
-

Top Strategies for Enhancing Circuit Breaker Performance and Reliability in Industrial Applications
-

7 Essential Tips for Optimizing Your Electric Motor VFD Efficiency
-

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding 3 Phase Electric Motors: Efficiency, Applications, and Benefits
-

How to Optimize Energy Efficiency with Variable Frequency Drives in Your Facility
