What is a Motor Control Center and How Does It Improve Efficiency in Industries
In today's fast-paced industrial landscape, efficiency and reliability in power distribution are paramount. One integral solution to achieving these objectives is the motor control center (MCC), a centralized system designed to control and monitor electric motors effectively. According to John Smith, a leading expert in industrial automation, "The motor control center plays a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency by streamlining the management of motor systems." This statement underscores the importance of MCCs in optimizing industrial processes.
Motor control centers not only serve as a hub for motor management but also contribute significantly to energy savings and maintenance reduction. By providing real-time data and monitoring capabilities, MCCs allow industries to quickly respond to operational changes and maintenance needs. As companies strive for greater sustainability and cost-effectiveness, the adoption of an efficient motor control center becomes increasingly essential to stay competitive in the global market. The potential benefits of increased efficiency and decreased downtime make the motor control center a vital asset for modern industries.
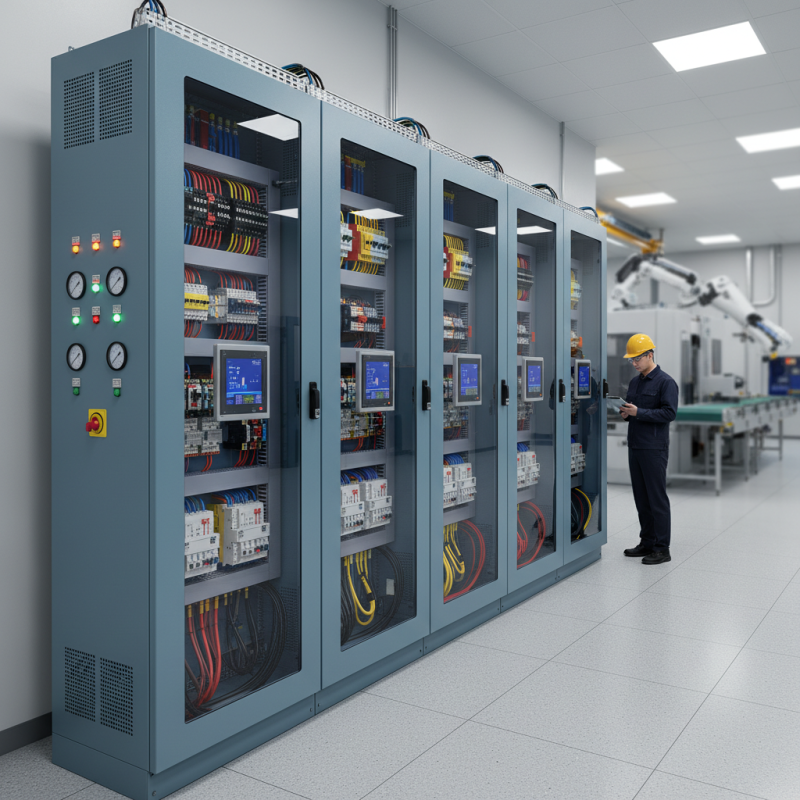

What Is a Motor Control Center and Its Core Components
A Motor Control Center (MCC)
A Motor Control Center (MCC) is a centralized assembly that houses motor control units, electrical components, and safety equipment, ensuring efficient control of electric motors in industrial settings. Its core components typically include motor starters, circuit breakers, contactors, overload relays, and control panels. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in managing the power supply, protecting equipment from faults, and facilitating user interaction with the control systems.
The motor starters serve to start and stop the motors, while circuit breakers protect the electrical circuits from overload or short circuits. Contactors allow for the remote operation of motors, enabling operators to control multiple motors from a single location. Additionally, overload relays monitor motor currents to prevent overheating and damage. The control panels provide operators with vital information regarding the operational status of the motors, enabling them to make quick decisions to enhance efficiency. Together, these components contribute to a streamlined process, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity in industrial operations.
The Role of Motor Control Centers in Industrial Automation
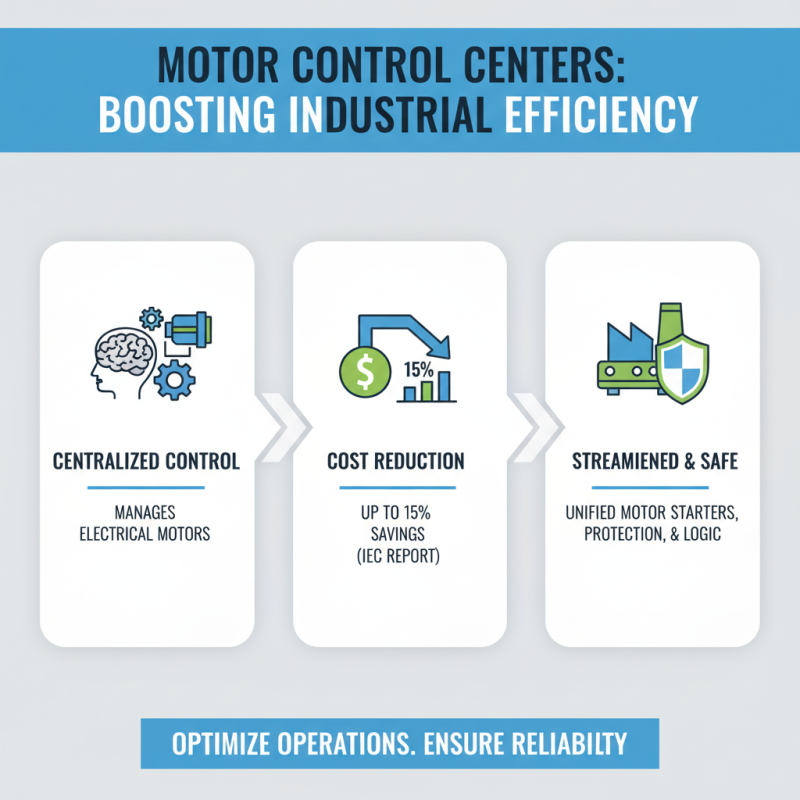
Motor Control Centers (MCCs) play a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency within industrial automation. These centralized systems are designed to manage and control the electrical motors in various industrial processes, ranging from manufacturing to water treatment facilities. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the implementation of MCCs can lead to a reduction in operational costs by as much as 15% due to improved motor control and monitoring capabilities. By consolidating motor starters, protection devices, and control logic into a single location, MCCs streamline operations while ensuring the safety and reliability of machinery.
The efficiency gains achieved through MCCs are particularly significant in terms of energy consumption. The U.S. Department of Energy highlights that optimizing motor systems can lead to energy savings of 20-50% across various applications. This is crucial as motors consume nearly 70% of the total electricity used in industrial facilities. With advanced features such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) and real-time data analytics, MCCs enhance the performance of motor systems, allowing for precise control and automation. This not only minimizes downtime but also maximizes the operational lifespan of equipment, contributing to overall production efficiency. As industries continue to evolve towards smart manufacturing, the role of Motor Control Centers will only become more central in driving operational excellence and sustainability.
Benefits of Implementing Motor Control Centers in Industries
Motor Control Centers (MCCs) play a crucial role in enhancing industrial efficiency by centralizing the control of multiple motor-driven applications. One of the primary benefits of implementing MCCs is improved operational safety. By providing a dedicated space for motor management, MCCs reduce the risk of electrical hazards. Operators can monitor and control equipment from a safe distance, which minimizes the risk of accidents and injuries in the workplace.
Another significant advantage is the ability to achieve better energy management. MCCs often incorporate advanced features such as variable frequency drives (VFDs) that optimize motor performance according to demand. This leads to significant energy savings and reduced operational costs. Additionally, the centralized control allows for real-time monitoring and diagnostics, enabling prompt maintenance interventions. This proactive approach not only prolongs the lifespan of equipment but also minimizes downtime, ensuring consistent production processes. Through these advantages, industries that adopt Motor Control Centers can achieve heightened operational efficiency and productivity.
How Motor Control Centers Enhance Operational Efficiency
Motor Control Centers (MCCs) play a crucial role in enhancing operational efficiency across various industries. By centralizing the control of motors and related equipment, MCCs streamline various processes within a facility. This centralized management allows for quick access to vital information regarding motor status, power usage, and operational anomalies. With real-time monitoring capabilities, industries can proactively address issues, reducing downtime and ensuring a smoother workflow.
Furthermore, MCCs contribute to energy efficiency by enabling precise control over motor operations. By incorporating advanced technologies such as variable frequency drives (VFDs), facilities can optimize motor speed and torque based on specific operational needs, thereby minimizing energy waste. This capability not only supports sustainable practices but also significantly reduces operational costs. Enhanced diagnostics and predictive maintenance features embedded in modern MCCs also empower plant operators to foresee potential failures, avoiding costly repairs and unexpected interruptions in production.
What is a Motor Control Center and How Does It Improve Efficiency in Industries
| Feature | Description | Efficiency Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Consolidation of Control Equipment | Motor control centers house multiple motor control devices in one package. | Reduces footprint and minimizes installation time and costs. |
| Centralized Control | Provides a central location for monitoring and controlling motors. | Enhances operator awareness and quick response to issues. |
| Enhanced Safety Features | Includes protective devices to prevent overloads and short circuits. | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs due to fewer accidents. |
| Energy Efficiency | Employs advanced technology to optimize motor operation. | Lowers energy consumption and operating costs. |
| Remote Monitoring | Allows for monitoring and control from remote locations. | Facilitates timely responses to operational conditions and reduces labor costs. |
Future Trends in Motor Control Centers and Industry Innovation
As industries evolve, the future of Motor Control Centers (MCCs) is poised for significant innovation, driven by advancements in technology and the need for greater efficiency. One of the most notable trends is the integration of smart technologies and IoT (Internet of Things) within MCCs. This shift allows for real-time monitoring and data analytics, enabling operators to optimize performance, reduce energy consumption, and anticipate maintenance needs.
By harnessing data-driven insights, industries can enhance operational efficiency and minimize downtime, ultimately leading to substantial cost savings.
Another emerging trend is the move towards modular and flexible MCC designs. As manufacturing processes become increasingly complex and customizable, businesses require motor control solutions that can adapt rapidly to changing demands. Future MCCs will likely feature modular components that can be easily reconfigured or expanded, allowing industries to respond swiftly to market fluctuations. Furthermore, advancements in energy-efficient technologies will reshape MCC functionality, promoting sustainable practices and reducing the overall environmental impact of industrial operations. This evolution not only aligns with global sustainability goals but also enhances the overall resilience and adaptability of industrial setups.
Related Posts
-

7 Tips to Optimize Your Motor Control Systems for Increased Efficiency
-

Essential Guide to Optimizing Industrial Motors with 3 Phase Soft Starters
-

Unlocking Energy Efficiency: The Role of Variable Frequency Motor Controllers in Modern Industries
-
Understanding the Future of Motors and Controls in Sustainable Technology
-

2025 Top 5 Motor Soft Starter Options for Efficient Energy Management
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Manual Motor Starters for Electrical Applications
