Understanding Motor Starters: Essential Components for Industrial Engine Control
In the realm of industrial engine control, the motor starter plays a pivotal role in ensuring the efficient and reliable operation of electric motors. It serves as a crucial interface between the electrical supply and the motor, enabling the safe and effective starting, stopping, and protection of the motor system. Understanding the various types of motor starters—such as direct-on-line (DOL) starters, star-delta starters, and soft starters—equips engineers and technicians with the knowledge needed to select the appropriate starter for specific applications. Each type offers unique benefits and functionalities tailored to different operational requirements.
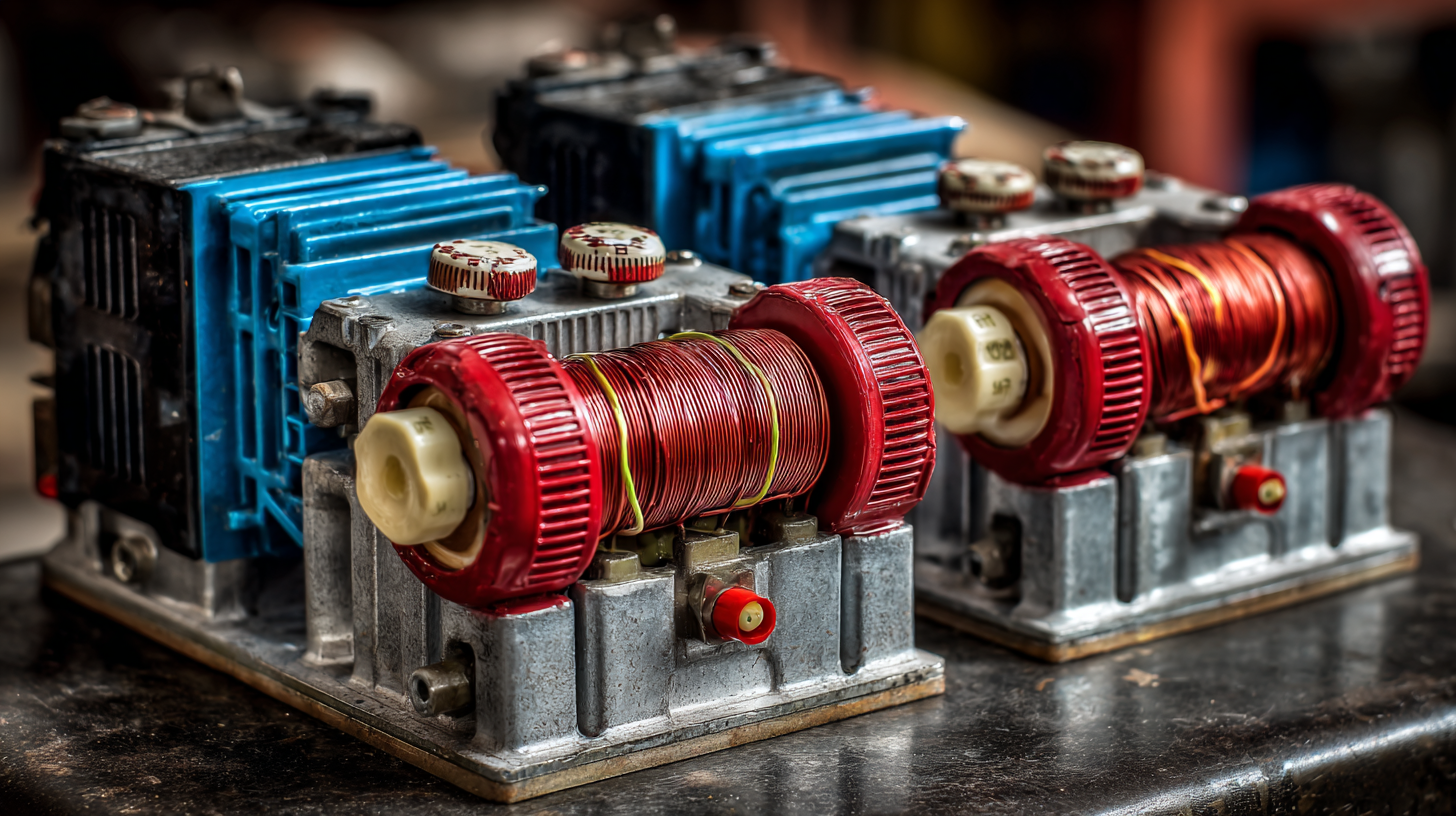
As industries increasingly rely on automation and advanced machinery, a comprehensive grasp of motor starters and their essential components becomes indispensable in optimizing performance, enhancing safety, and prolonging the longevity of industrial equipment. This article delves into the intricacies of motor starters, shedding light on their fundamental characteristics and the critical role they play in modern industrial systems.
How to Choose the Right Motor Starter for Your Industrial Application
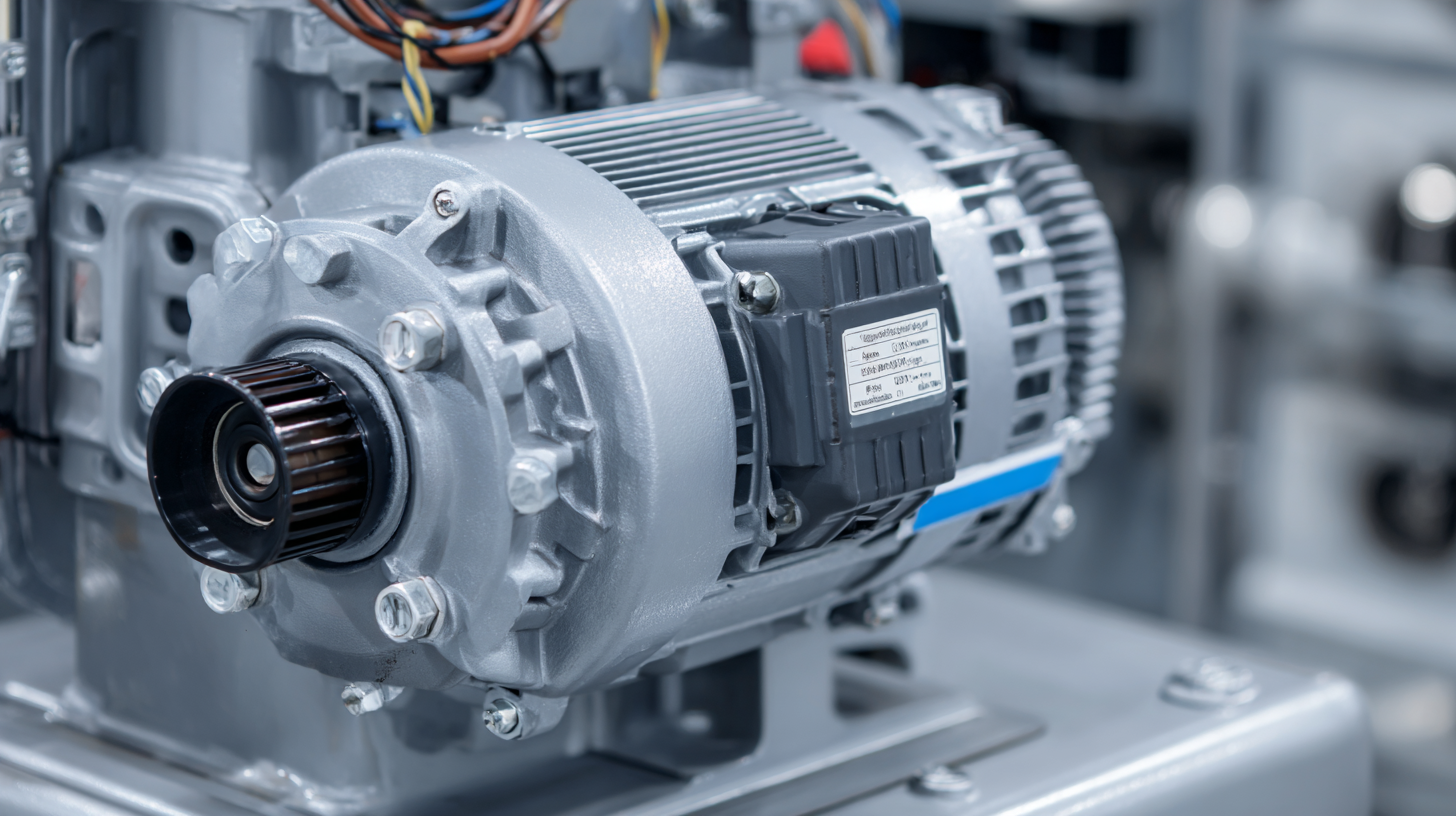 Choosing the right motor starter for your industrial application is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient operation of motors. Motor starters come in various types, including direct-on-line, star-delta, and soft starters, each suited for specific applications. Understanding the requirements of your motor—such as voltage, load type, and starting conditions—is essential in making an informed decision.
Choosing the right motor starter for your industrial application is crucial for ensuring reliable and efficient operation of motors. Motor starters come in various types, including direct-on-line, star-delta, and soft starters, each suited for specific applications. Understanding the requirements of your motor—such as voltage, load type, and starting conditions—is essential in making an informed decision.
Tips: Always assess the power ratings and inrush currents of your motors to select a starter that can handle these demands without failure. Additionally, consider the environmental conditions where the motor operates, as this can affect the components' durability and performance.
When selecting a motor starter, it’s important to factor in additional features for enhanced control and safety. Some starters come with built-in overload protection and monitoring capabilities, which can prevent damage from voltage spikes or overheating. These features can significantly prolong the lifespan of your equipment and reduce maintenance costs.
Tips: Look for starters with adjustable settings to fine-tune performance based on specific operational needs. Always refer to the manufacturer's guidelines to ensure compatibility and compliance with your industrial standards.
Understanding the Key Components of Motor Starters for Effective Control
Motor starters play a critical role in the control of industrial engines, providing both safety and efficiency. Understanding the key components of motor starters can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your control systems. At the core of a motor starter is the contactor, which acts as a switch to control the power supply to the motor. Pairing it with overload relays helps to protect the motor from overheating by cutting off power in case of excessive current draw.
**Tips:** When selecting a motor starter, ensure that the contactor ratings match the motor specifications to avoid under or over-sizing. Additionally, consider integrating thermal overload protection for different operational environments, which can improve the lifespan of the motor.
Another vital component is the control circuit, typically comprised of push buttons, terminals, and fuses. This circuit allows for manual control of the motor, enabling operators to start and stop the engine safely. An effective control circuit design maximizes safety features and operational reliability.
**Tips:** Regularly test and maintain the control circuit components to ensure responsive operation. Implementing indicator lights can also provide quick visual feedback on motor status, enhancing operational oversight.
Understanding Motor Starters: Essential Components for Industrial Engine Control
| Component | Function | Specifications | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contactors | Control the power to the motor by opening and closing electrical circuits | Current rating: Up to 800A; Voltage rating: 600V AC | Industrial motors, HVAC systems |
| Overload Relays | Protect motors from overheating by cutting off the power if current exceeds predefined limits | Adjustable trip settings; Typically 1A - 80A | Pumps, conveyors, fans |
| Push Buttons | Manually control motor operation (start/stop) | Rated voltage: 24V, 120V, 240V; Rated current: 10A | Control panels, machinery |
| Starters | Provide a means to start and stop motors safely | Types: Direct, Star-Delta; Voltage rating: up to 690V | Factories, industrial equipment |
| Control Circuit | Connect components like push buttons, timers, and relays for automation | Control voltage: 24V AC/DC; Wire gauge: 18-14 AWG | Industrial automation systems |
How to Optimize Motor Starter Performance to Enhance Energy Efficiency
Motor starters play a vital role in optimizing industrial engine control, contributing significantly to energy efficiency. By incorporating advanced power factor correction (PFC) technology, these systems ensure that electrical energy is utilized more effectively, reducing waste and improving overall performance. The shift towards renewable energy sources and sustainability in manufacturing is amplifying the demand for such innovations.
As industries increasingly adopt automation, motor starters equipped with cutting-edge sensors and smart control technologies can help streamline operations, enhancing both productivity and energy savings.
The integration of multifunctional motor control and thermal management solutions is essential in this evolving landscape. New developments focus on creating compact and efficient systems, crucial for applications in electric vehicles and industrial automation. As companies continue to innovate in motor starter design, the emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainable practices will drive performance enhancements. This alignment not only meets regulatory standards but also benefits businesses by lowering operational costs and reducing their carbon footprint.
Essential Maintenance Practices for Prolonging Motor Starter Lifespan
Maintaining motor starters is crucial for ensuring their longevity and optimal performance in industrial applications. Regular inspections play a key role in this process. Engineers should conduct periodic checks for signs of wear and tear, including degraded electrical contacts, corrosion, and mechanical malfunctions. By identifying and addressing these issues early, costly repairs and unexpected downtimes can be minimized, allowing the machinery to operate smoothly.
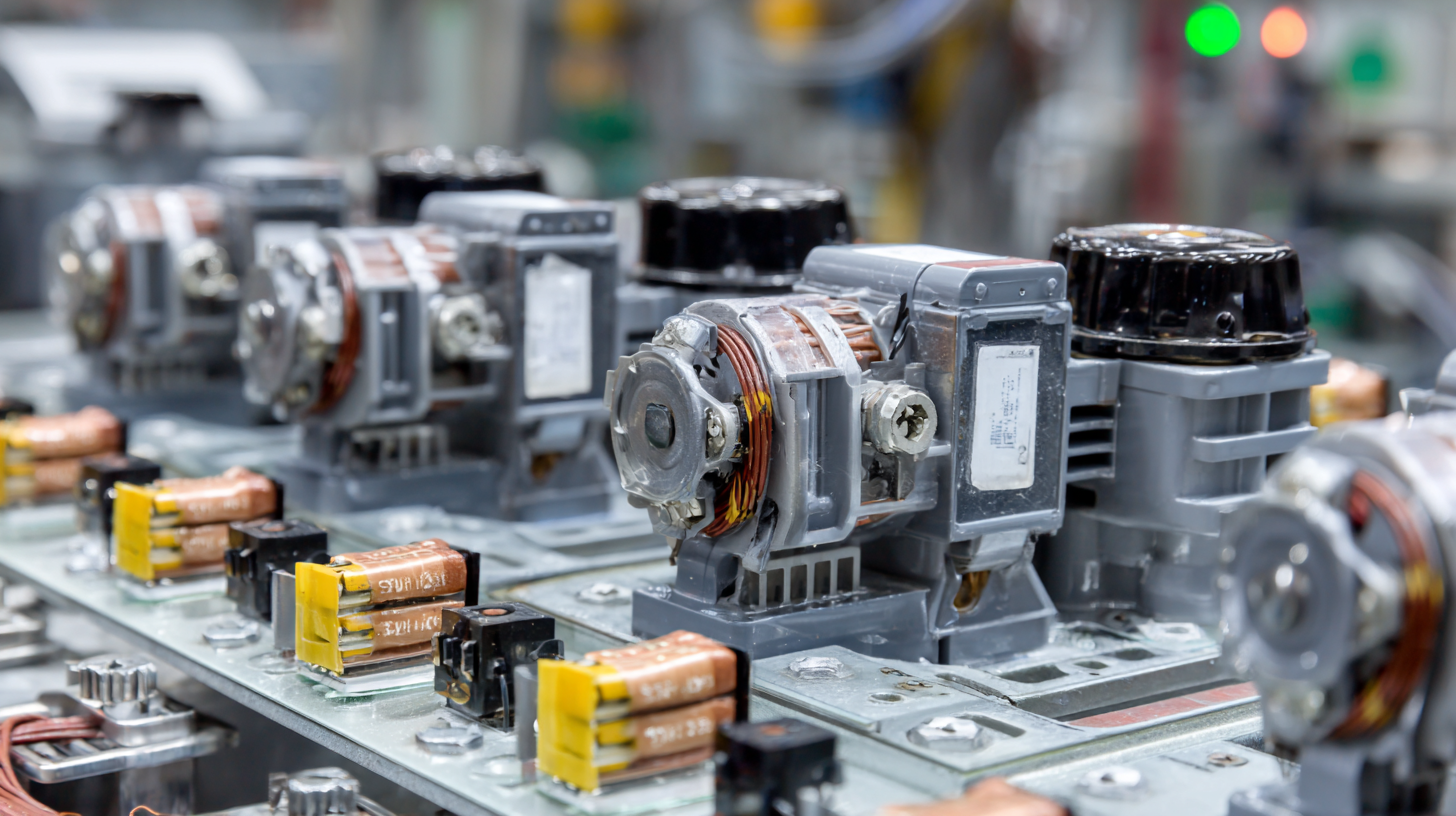
In addition to regular inspections, cleaning and lubrication are essential maintenance practices. Dust and debris can accumulate in motor starters, potentially hindering their performance. It is important to keep these components clean to prevent overheating and failure. Lubricating moving parts ensures they operate without friction, prolonging their life span. Implementing a routine maintenance schedule that includes these practices not only enhances reliability but also maximizes the efficiency of industrial engine control systems.
How to Troubleshoot Common Issues in Motor Starters for Industrial Machinery
When troubleshooting common issues in motor starters for industrial machinery, it's essential to have a systematic approach. A frequent problem encountered is the starter failing to engage the motor. This could be due to various reasons, including faulty control circuits, broken connections, or a malfunctioning overload relay. Begin by checking the power supply to the starter and ensure that all connections are secure. Inspect the control circuit for any signs of damage or wear, as even minor issues can disrupt functionality.
Another common issue is overheating, which can lead to premature failure of the motor starter. Overheating might stem from excessive current draw, inadequate ventilation, or a wrongly sized starter for the application. Monitoring the amperage levels when the motor is operational provides insight into whether the motor is operating within its specified range. If overheating persists, reassessing the load conditions and the starter's size is necessary to ensure they match the operational requirements of the machinery. Regular maintenance practices, such as cleaning components and checking for wear, can also help mitigate these issues and extend the life of motor starters in industrial settings.
Related Posts
-

How to Optimize Energy Efficiency with Variable Frequency Drives in Your Facility
-

7 Essential Tips for Optimizing Your Electric Motor VFD Efficiency
-

How to Choose the Right Circuit Breaker for Your Home Electrical System
-

5 Essential Benefits of Upgrading Your Electrical Switchgear for Global Industry Leaders
-

7 Tips to Optimize Your Motor Control Systems for Increased Efficiency
-

Essential Guide to Optimizing Industrial Motors with 3 Phase Soft Starters
