Top 10 Electric Motor Controllers You Should Consider?
Electric motor controllers are crucial in various applications. They manage the flow of energy to electric motors. Whether in electric vehicles or industrial machines, these controllers play a key role. Alex Johnson, an expert in the electric motor controller industry, once said, "The right controller can make or break a system's performance."
Choosing the right electric motor controller is not straightforward. Different motors require different controllers. Factors like efficiency and performance must be evaluated. Some products may not meet long-term needs. It’s essential to reflect on how these choices impact overall system efficiency.
There are numerous options available. Some controllers are user-friendly, while others require advanced understanding. Every choice carries potential drawbacks. Understanding these factors can greatly enhance decision-making. An informed choice leads to better performance and longevity in your electric motor systems.
Top 10 Electric Motor Controllers: Key Features and Specifications
When selecting the right electric motor controller, several key features should be examined. Efficiency is paramount. Many industry reports indicate that the most efficient controllers can reach efficiencies over 95%. This efficiency translates directly to energy savings. A well-designed controller can reduce operational costs significantly.
Another critical specification is the control method. PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and scalar control are popular choices. PWM offers better speed control, which enhances performance. Scalar control, while simpler, may not achieve the same precision. Manufacturers often provide data on the responsiveness of these methods, highlighting how they impact the overall system performance.
User interfaces also play a major role in functionality. Controllers equipped with intuitive displays allow for real-time monitoring. This feature can aid in troubleshooting, saving time and money. Reportedly, systems with user-friendly interfaces tend to have lower operational errors. However, complexity can lead to challenges. Balancing high-tech features with usability is still a design dilemma. Some users find themselves overwhelmed by options, leading to confusion and inefficiency.
Understanding Different Types of Electric Motor Controllers and Their Applications
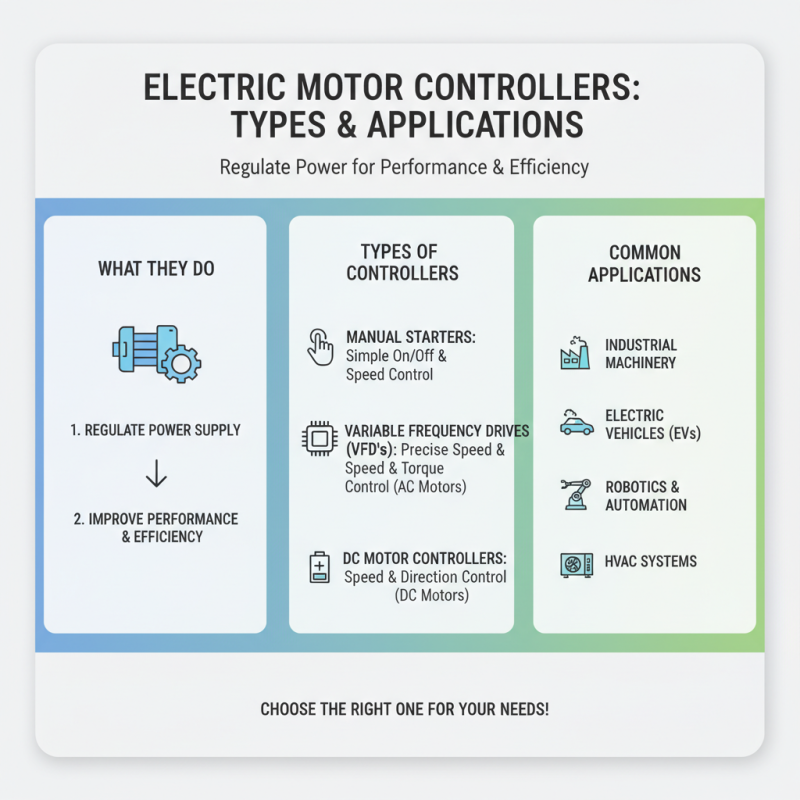
Electric motor controllers are vital in various applications. They regulate the power supplied to electric motors, impacting performance and efficiency. Understanding the types available can help you choose the right one for your needs.
There are several types of electric motor controllers. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controllers offer efficient control for DC motors. They work by varying the duty cycle, thereby adjusting speed and torque. In contrast, sensored controllers provide precise control for applications requiring accuracy. These are ideal for robotics and CNC machines.
Another type is sensorless controllers, which can save costs. However, they may not perform well at low speeds. Some users find them difficult to fine-tune. On the other hand, AC controllers are perfect for industrial applications, handling higher power levels. Each type has pros and cons. It can be tricky to determine which is best for your project.
Market Trends: Growth Statistics and Demand for Electric Motor Controllers

The demand for electric motor controllers is surging. Various reports anticipate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 5.8% from 2023 to 2030. This growth is driven by increased automation in industries. The rise in electric vehicles also plays a significant role. In fact, the market for electric vehicle-related technologies is projected to reach $300 billion by 2025.
However, challenges remain. The integration of advanced algorithms can be complex. Many companies express concerns about the high costs of development. Reports indicate that operational efficiency remains an area needing improvement. This gap can impact market growth. A closer look at the statistics reveals that organizations are investing more in R&D. In 2022, over 40% of industry players increased their technology budgets specifically for motor controllers.
The shift toward renewable energy sources is also significant. Utility companies are embracing electric motors for efficiency. This trend hints at a potential doubling of demand for motor controllers in the next decade. Yet, there is an ongoing struggle with the standardization of technologies. Without uniform guidelines, widespread adoption may face hurdles. The electric motor controller market presents opportunities but also calls for strategic thinking and adaptation.
Comparative Analysis of Efficiency and Performance in Electric Motor Controllers
When selecting electric motor controllers, efficiency and performance are key factors to consider. Different controllers exhibit varying levels of energy consumption. Some may save more energy under specific loads, while others shine in high-performance scenarios. This fluctuation in efficiency can significantly affect the overall operation of an electric motor system.
One must also observe the heat dissipation characteristics. Controllers that run hot might suffer from decreased performance and longevity. It’s essential to ensure that the controller’s thermal management is adequate. Not every controller offers the best heat dissipation. Some may require additional cooling systems, adding complexity to the design.
Performance under various operating conditions is another aspect to evaluate. Controllers should maintain consistent performance regardless of the load. However, not all options perform well in diverse environments. This variance can lead to suboptimal results. A controller that works excellently in one situation might not fare well in another. Testing under actual operating conditions provides valuable insights. Ultimately, the right choice depends on specific requirements and desired outcomes.
Top 10 Electric Motor Controllers Efficiency Comparison
Future Innovations: Emerging Technologies in Electric Motor Controller Design
The world of electric motor controller design is on the brink of exciting innovations. Emerging technologies are paving the way for more efficient and powerful solutions. Many developers are exploring intelligent control systems. These systems use artificial intelligence to enhance performance. They learn from usage patterns and adjust accordingly.
Another fascinating trend is the integration of renewable energy sources. This approach helps in creating eco-friendly motor controllers. Solar power and wind energy are becoming more commonplace. These energy sources align well with sustainable practices.
However, some challenges remain. Not all designs are ready for mass production. Developers often face issues with scalability. Solutions need time and testing to prove their reliability. There's always room for improvement, prompting engineers to rethink their methods. The future holds great promise, but it’s also filled with questions that demand answers.
Top 10 Electric Motor Controllers You Should Consider
| Controller Model | Voltage Range (V) | Current Rating (A) | Efficiency (%) | Integrated Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 24-48 | 60 | 95 | Regenerative Braking, Thermal Protection |
| Model B | 36-72 | 80 | 92 | Bluetooth Connectivity, Adaptive Control |
| Model C | 12-60 | 40 | 90 | IP67 Rating, High Torque |
| Model D | 48-120 | 100 | 94 | Fuzzy Logic Control, Diagnostics |
| Model E | 24-96 | 93 | CAN Bus Support, User Interface | |
| Model F | 36-90 | 55 | 96 | Energy Recovery, Compact Design |
| Model G | 48-144 | 90 | 89 | Remote Monitoring, Fault Detection |
| Model H | 30-60 | 70 | 91 | Multimode Operation, Quick Config |
| Model I | 24-120 | 85 | 88 | HMI Support, Customizable Settings |
| Model J | 48-96 | 65 | 90 | Dual Voltage, High Response Time |
Related Posts
-
How to Optimize Electric Motor Controller Performance for Maximum Energy Efficiency
-
How to Choose the Right Electric Motor Controller for Your Project?
-
Exploring Electric Motor Controller Innovations at the 2025 China 138th Canton Fair
-

Top Electric Motor VFD Types for Optimal Performance and Efficiency?
-

Top 10 Industrial Motors: Key Features and Buying Guide for 2023
-

7 Tips to Optimize Your Motor Control Systems for Increased Efficiency
