Top 10 Types of Industrial Electric Motors You Need to Know about
Industrial electric motors are essential components across a wide range of industries, powering everything from conveyor belts to manufacturing machinery. Understanding the various types of industrial electric motors is crucial for engineers, technicians, and decision-makers who seek to optimize performance and energy efficiency in their operations. With advancements in technology, the diversity of motors available has grown, each designed to meet specific applications and operational requirements.
In this article, we will explore the top 10 types of industrial electric motors you need to know about. By gaining insight into these motors, you will be better equipped to select the right technology for your projects, enhance productivity, and reduce operational costs. Whether you're in the field of automation, HVAC, or heavy machinery, familiarizing yourself with these motors will provide you with the knowledge necessary to make informed choices and drive your business forward. Let's delve into the world of industrial electric motors and discover the key players that can elevate your operational effectiveness.

Types of Industrial Electric Motors: An Overview
Industrial electric motors are crucial components in a wide range of applications, driving various machines across different industries. Understanding the different types of electric motors is essential for selecting the right one for specific tasks. The primary categories include AC motors, DC motors, and their subtypes, each designed to meet specific operational requirements.
AC motors, commonly used in large industrial applications, are known for their durability and efficiency. Within this category, induction motors and synchronous motors are the most prevalent. Induction motors, in particular, are favored for their simplicity and low maintenance needs. On the other hand, DC motors offer excellent speed control and are often employed in applications requiring precise manipulation, such as robotics and conveyor systems. Brushless DC motors, a subtype, have gained popularity in applications requiring high reliability and efficiency due to their reduced wear and tear.
Beyond AC and DC motors, specialized types such as stepper motors and servo motors play significant roles in automation and control processes. Stepper motors are particularly effective in applications requiring precise positioning, such as 3D printing and CNC machines. Servo motors, known for their high performance and accuracy, are essential in automated systems where feedback loops are crucial for maintaining control over position and speed. Understanding these various types of industrial electric motors enables businesses to optimize their operations effectively.
Characteristics of AC Motors in Industrial Applications
AC motors play a vital role in industrial applications due to their robust performance and versatility. The characteristics of AC motors make them ideal for a variety of tasks, from powering conveyor systems to driving heavy machinery. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), more than 70% of industrial electric motors operate on AC power, highlighting their dominance in the sector. The ability of AC motors to maintain constant speed across diverse loads is a significant advantage, which is essential for applications that require consistent performance.
In addition to performance consistency, AC motors are known for their durability and low maintenance requirements. A study published by the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) indicates that AC motors typically have a lifespan of 15-20 years, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs over time compared to their DC counterparts. Furthermore, advancements in variable frequency drive (VFD) technology have enhanced the efficiency of AC motors, enabling precise control over speed and torque while optimizing power consumption. This adaptability not only increases operational efficiency but also contributes to energy savings, making AC motors a preferred choice in various industries focused on sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
A Deep Dive into DC Motors and Their Uses
DC motors, or direct current motors, are crucial components in various industrial applications due to their simplicity and efficiency. They operate on the principle of converting electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of magnetic fields. One of the significant advantages of DC motors is their ability to provide excellent speed control, making them ideal for applications that require precise adjustments. This feature is particularly beneficial in sectors like robotics, conveyor systems, and electric vehicles where maintaining a stable speed is essential.
Moreover, DC motors come in two primary types: brushed and brushless. Brushed DC motors use carbon brushes to conduct electricity to the rotor, offering straightforward design and maintenance, whereas brushless DC motors employ electronic controllers to enhance efficiency and reduce wear. This distinction not only affects their lifespan and performance but also their application scenarios. Brushless variants are often preferred in high-performance settings due to their higher efficiency and quieter operation, common in computer cooling fans and aerospace applications. In contrast, brushed motors are favored in applications where cost is a significant concern, such as in low-budget household appliances and small machinery.
Exploring Synchronous versus Asynchronous Motors
When delving into industrial electric motors, a critical distinction is between synchronous and asynchronous motors. Synchronous motors operate at a constant speed, which is synchronized with the supply frequency. This quality makes them ideal for applications requiring precise speed control and consistent performance, such as in manufacturing processes where timing is crucial. These motors often require additional components like excitation systems, which can add to their complexity, but they offer high efficiency and better power factor performance, especially in heavy-duty applications.
In contrast, asynchronous motors, primarily the widely used induction type, operate at varying speeds. The rotor does not rotate at the same speed as the stator's magnetic field; rather, it lags behind slightly, which allows for a simple and rugged design. This type of motor is favored for its ease of maintenance and lower cost, making it suitable for a plethora of applications in various industries, from HVAC systems to conveyor belts. The simplicity of their design also contributes to their robustness in demanding environments.
**Tips:** When deciding between synchronous and asynchronous motors, consider the specific requirements of your application. If your process demands high precision and stability in speed, a synchronous motor may be the best choice. However, if flexibility and ease of repair are your priorities, an asynchronous motor could serve you better. Always consult with experts to ensure you select the right motor for your needs. Additionally, factor in the operating environment, as it can significantly impact the longevity and performance of the motor.
Top 10 Types of Industrial Electric Motors You Need to Know about - Exploring Synchronous versus Asynchronous Motors
| Motor Type | Description | Efficiency (%) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Synchronous Motor | Operates at a constant speed that is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current. | 85-95 | Pumps, compressors, and conveyors. |
| Asynchronous Motor | Speed that varies with load; also known as an induction motor. | 70-90 | Fans, cranes, and industrial machinery. |
| Permanent Magnet Motor | Uses permanent magnets to create the magnetic field instead of windings. | 85-95 | Electric vehicles and robotics. |
| Stepper Motor | Divided into discrete steps, allowing for precise control of angular position. | 75-85 | 3D printers and CNC machines. |
| Servo Motor | A motor that provides precise control of angular position or speed. | 80-90 | Robotics and automation systems. |
| DC Motor | Converts direct current electrical energy to mechanical energy. | 70-85 | Electric vehicles and industrial applications. |
| Universal Motor | Can operate on either AC or DC supply; suitable for lower voltage applications. | 75-90 | Power tools and household appliances. |
| Linear Motor | Produces linear motion instead of rotational motion. | 80-90 | Maglev trains and industrial automation. |
| Brushed DC Motor | Uses brushes to deliver current to the motor windings. | 70-80 | Toys and small household appliances. |
| Brushless DC Motor | Eliminates brushes; electronic control improves efficiency. | 85-95 | Drones and high performance fans. |
Key Factors in Choosing the Right Industrial Motor
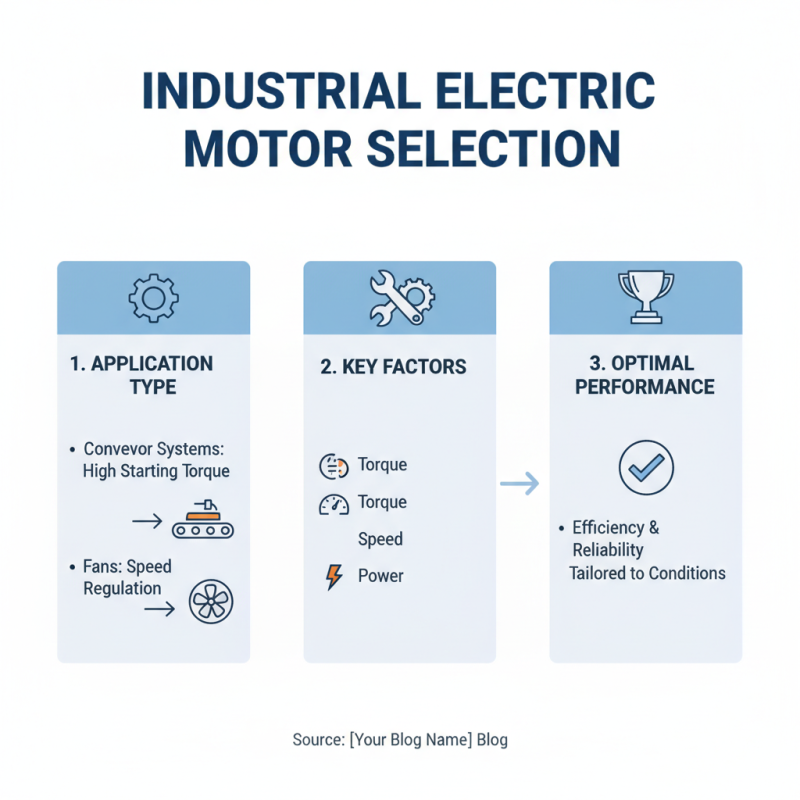
When selecting the right industrial electric motor, several key factors must be carefully considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. First, the application type plays a vital role in determining the appropriate motor. Different tasks may require varying levels of torque, speed, and power. For example, motors used in conveyor systems may demand high starting torque, while those in fans may prioritize speed regulation. Understanding the specific requirements of the application is essential for selecting a motor that will operate effectively under expected conditions.
Another crucial aspect to consider is the environment in which the motor will operate. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to dust or corrosive substances can significantly influence the motor's lifespan and reliability. Certain motors are designed for harsh environments, featuring protective enclosures and materials that can withstand challenging conditions. Additionally, energy efficiency and compliance with regulatory standards should not be overlooked. Opting for high-efficiency motors can lead to long-term cost savings and reduced energy consumption, making them an environmentally friendly choice that aligns with modern sustainability goals.
Related Posts
-
Exploring Electric Motors Innovations at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

What Are the Latest Innovations in Electric Motors Driving Industry Efficiency and Sustainability
-

2025 Top 5 Electric Motors Revolutionizing Energy Efficiency and Performance
-

How to Choose the Right 3 Phase Electric Motor for Your Needs
-

7 Essential Tips for Optimizing Your Electric Motor VFD Efficiency
-
Understanding the Role of 3 Phase Electric Motors in Modern Industrial Applications
